CLINICAL,FORENSIC,AND ETHICS CONSULTATION IN MENTAL HEALTH
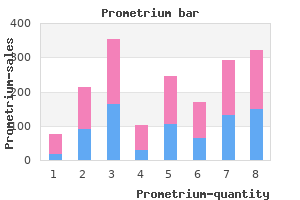
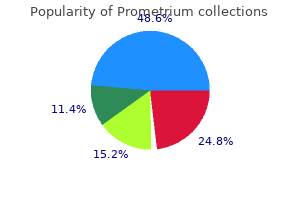
Prometrium
"200mg prometrium for sale, treatment lichen sclerosis".
By: X. Reto, M.B.A., M.D.
Medical Instructor, Washington State University Elson S. Floyd College of Medicine
Its efferents are anterior medications look up buy prometrium online pills, draining to the anterior diaphragmatic nodes close to the junctions of the seventh rib and cartilage; middle symptoms zollinger ellison syndrome discount prometrium on line, draining to nodes on the oesophagus and around the finish of the inferior vena cava; and posterior hb treatment buy prometrium us, draining to nodes across the aorta on the point where it leaves the thorax treatment lead poisoning order prometrium 100 mg without a prescription. The stomach plexus anastomoses with the hepatic lymphatics and peripherally with these of the subperitoneal tissue. Efferents from its proper half finish in a bunch of nodes on the inferior phrenic artery, or in the proper lateral aortic nodes. Those from the left half of the belly diaphragmatic plexus move to the pre-aortic, lateral aortic and terminal oesophageal nodes. Those superficial to trapezius and latissimus dorsi unite to type 10 or 12 trunks, which end in the subscapular nodes. Those in the pectoral area, together with vessels from the pores and skin covering the periphery of the breast and its subareolar plexus, run again, collecting those superficial to serratus anterior, to attain the pectoral nodes. Vessels near the lateral sternal margin pass between the costal cartilages to the parasternal nodes and anastomose throughout the sternum, providing a route for contralateral nodal unfold in medially positioned breast carcinoma. A few vessels from the upper pectoral region ascend over the clavicle to the inferior deep cervical nodes. Lymph from the deeper tissues of the thoracic walls drains primarily to the parasternal, intercostal or diaphragmatic nodes. The higher eleven lie between the ribs (intercostal nerves) and the twelfth lies below the final rib (subcostal nerve). The first two nerves provide fibres to the Anterior cutaneous branch Parasternal (internal thoracic) nodes There are four or five parasternal nodes along each inner thoracic artery on the anterior ends of the intercostal spaces. They drain afferents from the breast, deeper constructions of the supra-umbilical anterior abdominal wall, the superior hepatic surface (through a small group of nodes behind the xiphoid process) and deeper parts of the anterior thoracic wall. Their efferents often unite with these from the tracheobronchial and brachiocephalic nodes to form the bronchomediastinal trunk. The latter might open on either side, instantly into the jugulosubclavian junction, into both nice vein near the junction, the best subclavian trunk or lymphatic duct, or the thoracic duct on the left. They obtain deep lymph vessels from the posterolateral aspects of the chest wall and breast, a few of which are interrupted by small lateral intercostal nodes. Efferents of nodes in the decrease 4�7 spaces unite right into a trunk that descends to the stomach confluence of lymph trunks or to the beginning of the thoracic duct. Efferents of nodes in the left higher spaces finish within the thoracic duct; these of the right upper spaces end in one of the right lymph trunks. Lateral cutaneous branch Recurrent nerve to vertebral canal Sympathetic ganglion Rami communicantes Intercostal nerve (ventral ramus) Diaphragmatic nodes Located on the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, these nodes are organized in anterior, proper and left lateral, and posterior groups. Dorsal ramus Subcostalis Anterior group the anterior group consists of two or three small nodes behind the base of the xiphoid process, draining the convex hepatic surface, and one or two nodes on each side close to the junction of the seventh rib and cartilage, which receive anterior lymph vessels from the diaphragm. Communicating branches link the intercostal nerves posteriorly within the intercostal spaces, and the lower five nerves talk freely within the belly wall. Twelfth thoracic ventral ramus (subcostal nerve) the ventral ramus of the twelfth thoracic nerve (subcostal nerve) is bigger than the others and gives a communicating branch to the primary lumbar ventral ramus (sometimes termed the dorsolumbar nerve). Like the intercostal nerves, it quickly offers off a collateral department and then accompanies the subcostal vessels along the inferior border of the twelfth rib, passing behind the lateral arcuate ligament and kidney, and in entrance of the higher a part of quadratus lumborum. It perforates the aponeurosis of the origin of transversus abdominis and passes forwards between that muscle and internal indirect, to be distributed in the same method because the decrease intercostal nerves. The subcostal nerve connects with the iliohypogastric nerve of the lumbar plexus and sends a department to pyramidalis. Its lateral cutaneous department pierces the inner and exterior oblique muscle tissue and supplies the lowest slip of the latter. First to sixth thoracic ventral rami the first thoracic ventral ramus divides unequally: a large branch ascends across the neck of the primary rib, lateral to the superior intercostal artery, to enter the brachial plexus, and a smaller department (the first intercostal nerve) runs in the first intercostal house and terminates as the first anterior cutaneous nerve of the thorax. A lateral cutaneous branch pierces the chest wall anterior to serratus anterior and provides the axillary skin; it might communicate with the intercostobrachial nerve and generally joins the medial cutaneous nerve of the arm. The first thoracic ramus usually receives a connecting ramus from the second, which ascends in front of the neck of the second rib. The second to sixth thoracic ventral rami move forwards of their intercostal spaces below the intercostal vessels. Posteriorly, they lie between the pleura and exterior intercostal membranes, but they run primarily between the internal intercostals and the subcostales/innermost intercostals. Near the sternum, they cross anterior to the interior thoracic vessels and transversus thoracis, pierce the internal intercostals, the external intercostal membranes and pectoralis main, and terminate because the anterior cutaneous nerves of the thorax.
Vascular provide Biceps brachii is usually provided by as a lot as symptoms 3 dpo order prometrium 100 mg fast delivery eight vessels originating from the brachial artery in the middle third of the arm treatment yeast infection men buy generic prometrium. These vessels pass laterally symptoms 6 days past ovulation 200 mg prometrium overnight delivery, posterior to the median nerve medicine 627 order 200mg prometrium with visa, and divide into ascending and descending branches simply before reaching the deep floor of the muscle. Smaller branches come up from the anterior circumflex humeral artery and the deltoid branch of the acromial divi sion of the thoracoacromial axis. The primary arterial provide might originate from the superior or inferior ulnar col lateral arteries, subscapular artery, axillary artery, ulnar or radial arteries in circumstances of proximal bifurcation of the brachial artery, or the profunda brachii artery. There is usually a single massive pedicle, attending the nerve to biceps; damage to the muscle and musculocutaneous nerve at this level within the arm generally ends in a fibrotic, atonic muscle with distal sensory dysfunction. Testing Teres major can be palpated posterior to the posterior axillary fold during adduction of the humerus towards resistance. Rotator cuff disease 824 the subacromial space is defined inferiorly by the superior floor of the rotator cuff (supraspinatus and the anterior a half of infraspinatus); superiorly by the anterior edge and inferior surface of the anterior third of the acromion, coracoacromial ligament and acromioclavicular joint, forming the coracoacromial arch; and posteriorly by the posterior wall of the subacromial bursa. It is occupied by the subacromial bursa, lined by synovial membrane, that extends anterolaterally under deltoid as the subdeltoid bursa, and which facilitates motion of the rotator cuff under the coracoacromial arch. The higher floor of the rotator cuff normally impinges, without signs, underneath the coracoacromial arch when the humerus is abducted, flexed and medially rotated. Innervation Biceps brachii is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, C5 and 6, with separate branches passing to every stomach. Actions Biceps brachii is a robust supinator, especially in rapid or resisted actions. It flexes the elbow � most successfully, with the forearm supinated � and acts, to a slight extent, as a flexor of the shoulder joint. The lengthy head helps to check upward translation of the humeral head during contraction of deltoid, in synergy with the motion of the rotator cuff. It is connected, via the bicipital aponeu rosis, to the posterior border of the ulna, the distal end of which is drawn medially in supination. When the elbow is flexed towards Shoulder girdle and arm Pain is generated during abduction of the arm in the scapular airplane; typically, an arc of pain is skilled (between 60� and 120� of eleva tion, the impingement arc). Rotator cuff illness is a painful situation with a multifactorial aetiology, in which extreme or persistent impingement of the rotator cuff tendons on the undersurface of the coracoacromial arch is often a major factor. The supraspinatus tendon is anatomi cally affected most by the impingement, which coincides with an space of lowered vascularity in this tendon. When related to a tendin opathy from agerelated degenerative adjustments within the tendon, impingement may be related to partial or full tears of the cuff. Clinically, this situation causes tenderness over the anterior portion of the acromion, and pain that typically happens on abducting the shoulder between 60� and 120� (the painful arc). Lowering the hand under the affect of gravity by extension on the elbow requires managed lengthening of biceps brachii. This is an instance of a recurring motion by which muscle tension increases despite rising length. B Basilic vein Ulnar nerve Radial artery and nerve Testing With the forearm supinated, biceps brachii can be tested by palpating its fibres during elbow flexion against resistance. Brachialis Attachments Brachialis arises from the lower half of the anterior floor of the shaft of the humerus, starting on both facet of the inser tion of deltoid, and lengthening distally to inside 2. In some cases, it sends a tendinous slip to the radius or to the bicipital aponeurosis. Relations Biceps, the brachial vessels and the musculocutaneous and median nerves are anterior. Pronator teres and the medial intermuscular septum, which separates it from triceps and the ulnar nerve, are medial. The radial nerve, radial recurrent and radial collateral arteries, brachioradia lis and extensor carpi radialis longus are all lateral. Vascular supply the blood provide to brachialis sometimes consists of two major arteries (superior and inferior), supplemented by a system of accessory arteries.
Generic prometrium 200mg on-line. Colorectal polyps - causes symptoms diagnosis treatment pathology.
Towards the aortic orifice treatment centers buy cheap prometrium 100 mg online, the septum turns into the thin and collagenous interventricular part of the membranous septum medicine pacifier purchase prometrium 200 mg on line, an oval or round area below and confluent with the fibrous triangle separating the best and the non-coronary leaflets of the aortic valve symptoms schizophrenia purchase 100mg prometrium visa. Between the inferior limits of the free margins of the leaflets of the mitral valve and the ventricular apex symptoms mold exposure purchase prometrium 100mg with mastercard, the muscular partitions exhibit deeper, finer and extra intricate trabeculae carneae than these of the proper ventricle, characteristically extra developed nearer the apex, and turning into smoother because the superior septal surface is reached. A, the oesophagus (O) passing behind the posterior left atrial wall and a broad left-lateral ridge (double-headed arrow). B, the part passes through the os of the left atrial appendage and the infolding of the ridge. The triangle signifies the carina or interpulmonary ridge between the higher and lower pulmonary veins. Thus it has an orifice with a supporting anulus, leaflets and quite a lot of chordae tendineae and papillary muscle tissue. Mitral valvular orifice the mitral orifice is a well-defined transitional zone between the atrial wall and the leaflet bases, being smaller than the tricuspid orifice (mean circumference is 9. The roughly round orifice is almost vertical and at 45� to the sagittal aircraft in diastole, but with a slight anterior tilt. Its ventricular facet faces anterolaterally to the left and slightly inferiorly in direction of the left ventricular apex. The mitral, tricuspid and aortic orifices are intimately connected at their central fibrous body. When the mitral valve leaflets close, they kind a single zone of coaptation, termed the commissure. Note the relationship of the leaflet insertions and the ventriculoarterial junction. C, the root of the aorta has been reduce open and distended, to be able to present the insertion of the semilunar leaflets. Note the zone of fibrous continuity between the leaflets of the aortic and mitral valves and their relationship to the fibrous trigones, and the semilunar attachment of the leaflets (compare with B). Echocardiography precisely assesses the diploma of thickening and its impact on systolic operate, similar to dynamic left ventricular outflow obstruction, systolic anterior motion of the aortic mitral valve leaflet and mid-systolic closure of the aortic valve. A variety of histological modifications are observed, including cardiomyocytic disarray with replacement fibrosis and collagenous part growth. Treatment is usually medical, apart from refractory instances and those in whom the left ventricular outflow tract obstruction has a gradient of greater than 50 mmHg. Catheter alcohol septal ablation has been introduced as a non-surgical various. A number of patients may require implantation of cardiac defibrillators to prevent sudden cardiac dying. In distinction, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy reveals asymmetric patterns of left ventricular hypertrophy, usually with sharp segmental transitions, left atrial enlargement and weird electrocardiographic patterns. The smooth-walled venous element of the left atrium is probably the most in depth part. The septal facet of the left atrium exhibits the crescentic line of the free fringe of the flap valve in opposition to the rim of the fossa ovalis. The orifices of the best superior and inferior pulmonary veins are adjacent to the aircraft of the septal aspect of the left atrium. The anulus is strongest on the inside elements of the left and right fibrous trigones. Between the prong tips, the atrial and ventricular myocardial lots are separated by a more tenuous sheet of deformable fibroelastic connective tissue. Mitral valve leaflets the mitral valvular leaflets have lengthy been described as paired structures. Its free edge bears a quantity of indentations, of which two are sufficiently deep and regular to be nominated as the ends of a solitary and oblique zone of apposition or 1008 commissure. These anteromedial (inferoseptal) and posterolateral (superoposterior) extremities may be regarded as two unbiased commissures, every positionally named as indicated in brackets. Although easy, the official names for these leaflets � anterior and posterior, respectively � are considerably misleading due to the obliquity of the valve.
More frequently medications 2355 buy prometrium 100 mg amex, it turns around the apex into the posterior interventricular groove and passes one-third to one-half of the way in which alongside its length treatment ibs buy prometrium 200mg, meeting the terminal twigs of the posterior (inferior) interventricular branches of the right coronary artery (see above) medicine 029 200mg prometrium amex. The anterior interventricular artery offers off proper and left anterior ventricular and anterior septal branches treatment zamrud order cheap prometrium, and a variable number of corresponding posterior branches. Anterior proper ventricular branches are small and infrequently quantity a couple of or two; the proper ventricle is equipped virtually entirely by the right coronary artery. Up to 9 massive left anterior ventricular arteries department at acute angles from the anterior interventricular artery, crossing the anterior facet of the left ventricle diagonally, with the largest reaching the rounded (obtuse) left cardiac border. One often dominates, typically arising individually from the left coronary trunk, which then ends by trifurcation. This left diagonal artery, reported to exist in at least 33�50% of hearts, could also be doubled (20%). A small left conal artery regularly leaves the anterior interventricular artery close to its origin, and anastomoses on the conus with its counterpart from the proper coronary artery and with the vasa vasorum of the pulmonary artery and aorta. The anterior septal perforating branches depart the anterior interventricular artery virtually perpendicularly, and cross posteroinferiorly throughout the septum, often supplying its ventral two-thirds. The first septal perforator artery usually supplies the atrioventricular bundle on the point of its division. Small posterior septal branches from the identical supply supply the posterior third of the septum for a variable distance from the cardiac apex (Loukas et al 2009). The circumflex artery, comparable to the anterior interventricular artery in calibre, curves left in the atrioventricular groove, and continues round the left cardiac border into the posterior part of the groove, terminating left of the crux in most hearts, although generally continuing because the posterior (inferior) interventricular artery. Smaller anterior and Details of coronary arterial distribution require integration into a concept of whole cardiac supply. Most generally, the right coronary artery provides all of the proper ventricle (except a small area to the right of the anterior interventricular groove); a variable a half of the diaphragmatic side of the left ventricle; the posteroinferior third of the interventricular septum; the right atrium and part of the left atrium; and the conduction system so far as the proximal components of the right and left crura. Left coronary distribution is reciprocal and includes most of the left ventricle; a slender strip of proper ventricle; the anterior two-thirds of the interventricular septum; and most of the left atrium. The term is deceptive because the left artery nearly at all times provides a higher volume of tissue than the best. In more than 50% of people, the proper atrium is equipped solely by the best coronary artery, and within the the rest the availability is dual. Posterior ventricular branches are smaller and fewer as a outcome of the left ventricle is partly provided by the posterior (inferior) interventricular artery. The artery to the sinu-atrial node is commonly derived from the anterior circumflex segment (less typically from the circum-marginal segment). The artery to the atrioventricular node, sometimes the terminal department of the circumflex artery (20%), arises near the crux. The extensive variation in frequency signifies that many bridges could additionally be asymptomatic during life. The main clinical circumstances produced by a myocardial bridge are cardiac ischaemia, atherosclerosis and sudden cardiac demise. The incidence of atherosclerosis is elevated when the best coronary artery is bridged. Although a relationship between myocardial bridges and sudden cardiac dying has not been established, autopsy series have proven histological proof of in any other case unexplained ischaemia in people with myocardial bridges; many died throughout exercise and had no different risk factors for coronary arterial disease. Arterial provide to the sinuatrial and atrioventricular nodes additionally varies: the sinu-atrial node is provided more typically by the right coronary artery; fewer than 10% of sinu-atrial nodes receive a bilateral provide. Acquired coronary artery fistulae are mostly iatrogenic in aetiology but may also happen after traumatic harm; these mostly are of the coronary cameral kind, from the proper coronary artery into the best aspect of the center. Coronary anastomoses the cardiac collateral circulation represents a local system for coronary arterial bypass. The first few centimetres of the arterial primary stems are devoid of anastomotic branches, however further distally, collateral channels are ample, exhibit variable calibres and occupy quite a few locations, permitting for bidirectional move between most native arteries. Anastomoses between branches of the coronary arteries, each subepicardial and myocardial, and between these arteries and extracardiac vessels, are of prime medical significance. Nevertheless, it has long been established that anastomoses do happen, particularly between fantastic subepicardial branches, they usually might improve during particular person life by mechanisms of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis. The anulus of Vieussens is a collateral vessel that crosses the subpulmonary infundibulum, providing an anastomosis between the conal department of the right coronary artery and the anterior interventricular artery. The artery to the sinu-atrial node commonly supplies a communication between the proximal parts of the coronary arteries.