CLINICAL,FORENSIC,AND ETHICS CONSULTATION IN MENTAL HEALTH
Cp-colchi
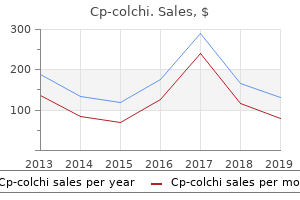
"Cost of cp-colchi, 0157 infection".
By: A. Darmok, M.A., M.D.
Clinical Director, Michigan State University College of Osteopathic Medicine
Memory ceases to be just in regards to the previous antibiotics for dogs and cats order cp-colchi 0.5 mg otc, and its prospective nature involves infection control certification cheap cp-colchi 0.5 mg with visa gentle antibiotic and pregnancy discount cp-colchi 0.5mg fast delivery. Thus antibiotics for urinary tract infection in dogs order cp-colchi with american express, a better way to define every of those interrelated functions is to consider the position every plays in this strategy of linking the previous to the lengthy run. That is the fundamental objective of memory- collecting related previous experience to anticipate future calls for and guide behav ior. These are thought to preserve a template of stimulus attributes which are related for current goals and thus to represent an necessary source of top- down, attention-related alerts that bias the analysis of incoming sensory stimulation (Desimone & Duncan, 1995). Accordingly, the present chapter will concentrate on the relation between working memory and a spotlight; however, it could be very important recognize that more distant traces from long-term reminiscence additionally affect the processing of incoming stimulation (see Aly & Turk-Browne, 2017; Awh, Belopolsky, & Theeuwes, 2012; Nobre & Mesulam, 2014; see determine 25. A secure internal cognitive state is required for integrating info over sensory discontinuities. Tonic delay exercise Single- unit neurophysiology within the awake, behaving monkey supplied influential Memory Forth the traces left behind by way of experience are the essence of memory. Attention attracts on previous expertise from a number of timescales to anticipate and prepare for incoming stimulation and guide adaptive motion. These mutual interactions feed a virtuous cycle that tunes our minds to essentially the most relevant options of the setting. Although a quantity of mnemonic timescales are essential for consideration, we concentrate on the interactions with working memory on this chapter. Findings from the basic single-unit delay- activity studies turn out to be more nuanced. For instance, exercise tends to increase during the delay in expectation of the probe (Watanabe & Funahashi, 2007) and might disappear altogether to reemerge on the anticipated time of the probe stimulus with out compromising per for mance (Watanabe & Funahashi, 2014). For instance, by using stimuli morphed alongside a number of dimensions, Freedman, Riesenhuber, Poggio, and Miller (2001) confirmed that neurons were selectively delicate to the size that monkeys were required to discriminate within the task. Similar effects have been found in the parietal cortex when monkeys had been required to discriminate between arbitrary categorical boundaries along steady characteristic dimensions (Freedman & Assad, 2006). Specifically, they told members that both the color or the orientation of a visual stimulus would be probed at the end of a memory delay. Patterns of exercise in the visual cortex selectively maintained the task-relevant characteristic, in preserving with a potential reminiscence code for guiding future behav ior. B, Decoding patterns of activity in early visible cortex, they discovered that activity within the reminiscence delay carried orientation- angle info when orientation was relevant for future decision-making or the color-hue information when shade was related. However, finer- grained evaluation of the qualitative patterns of brain exercise coding for particular gadgets reveals a much more dynamic picture (Stokes, 2015). The primary logic of machinelearning approaches to neural decoding could be extended to monitor qualitative modifications in coding format. Rather than evaluating the accuracy of decoding between two unbiased but equivalent units of data, decoding may be in contrast amongst data drawn from dif ferent contexts. For example, to check how neural coding evolves over time, decoding may be carried out in a method that checks the generalizability (or specificity) of discriminative patterns at dif ferent time points by training a classifier at one time point and testing per for mance at dif ferent time points. Similar dynamics are additionally seen with noninvasive electrophysiological methods in people (Myers et al. Information associated to the template was associated with a dynamically evolving sample of neural exercise. Rather than being tonically elevated, the sample became manifest around the predicted time of stimulus appearance. Rather than performing as a representational state that preserves the past as persistent exercise, it makes more sense to consider it as a practical neural state that shifts the coding properties of the system to anticipate future task calls for. Recent developments provide an expanding device box for exploring the practical properties of mnemonic states. The logic borrows from lively sonar, in which a well- characterised impulse (ping) is emitted towards a hidden panorama, and the contours are inferred from distortions in the reflected sign. In Nobre and Stokes: Memory and Attention: the Back and Forth 293 the case of neural sonar, we present a sensory impulse. We can infer modifications in the neural landscape from distortions within the output response (Wolff et al. Importantly, this strategy is theoretically sensitive to any change within the functional state of the focused system. A nice variety of other neurophysiological mechanisms might additionally play necessary roles (Barak & Tsodyks, 2014; Buonomano & Maass, 2009). Previous studies have discovered proof for a match-filter response, which alerts the diploma of match between the memory probe and the previous memory item.
To decide which model supplies probably the most appro priate description of the information antibiotics for acne dangers buy generic cp-colchi 0.5mg on line, we are in a position to subsequently simply choose the mannequin with the best marginal chance antibiotic shot cp-colchi 0.5mg overnight delivery. The ratio of the likelihoods is the Bayes factor home antibiotics for acne discount cp-colchi express, a mea positive of the evidence of 1 model over the opposite (Kass & Raftery infection urinaire buy cp-colchi 0.5 mg low cost, 1995). This strategy is valid for fashions that predict a hard and fast representational structure-that is, models primarily based on a single characteristic set with just one signal variance and noise variance pa rameter on the second stage. Under these circumstances, the mar ginal likelihood can serve as an approximation of the mannequin evidence-the likelihood of the data given the model. All secondlevel parameters may be effectively opti mized, as analytical derivatives of the marginal likeli hood with respect to these parameters are simply derived. An implementation of the corresponding algo rithms is openly out there (Diedrichsen, Yokoi, & Arbuckle, 2017). A central con cept in this method is the notion of a representational area (Guntupalli et al. Instead of thinking about voxel exercise profiles as points within the space of experimental situations (figure fifty six. The relation ship between the totally different activity patterns on this space defines the representation. Dissimilarity measures have the intuitive attraction of reflecting how strongly the distinction between two con ditions is represented in an space. That is, they inform us how properly a readout neuron that has access to the entire popu lation code may distinguish between the two condi tions. More generally, the representational geometry determines how well any characteristic that describes the underneath mendacity conditions might be read out. An especially useful dissimilarity measure is the crossvalidated estimate of the Mahalanobis distance (Diedrichsen & Kriegeskorte, 2017). This distance estimate is unbiased-that is, the expected worth of the dissimilarity is zero if two activity patterns only differ by noise. This relationship is due to the reality that all three approaches assess mannequin fit by comparing the second moment matrices of the exercise profile distributions. The only difference is that for a (co)variance matrix, the imply activity profile (across voxels) is subtracted before applying equation 56. A, the data include repeated mea sures of the same set of voxels throughout a spread of circumstances. Each column of the matrix constitutes an activity profile; each row an activity pattern across voxels. B, the activity profiles could be plotted within the house of the experimental conditions. The relation ships between exercise patterns in this excessive dimensional space outline the representational geometry (lines). D, Two views of a low dimensional projection of the representational geom etry of particular person finger movements in M1 (1, thumb�5, little finger) at four dif ferent movement speeds (black, slow�gray, fast). Although typically carried out, such subtractions are therefore not meaningful from a representational standpoint. Any significant imply exercise differences are subsequently captured in the secondmoment matrix. In sum, all three approaches define models by the second moment of the predicted activity profile distribution. The solely technical differ ence is how precisely the mismatch between the empiri cal and predicted secondmoment matrix is mea sured (Diedrichsen & Kriegeskorte, 2017). Using representational areas, one can visualize the representational geometry of a inhabitants code with out the need to outline a mannequin a priori. To be succesful of gener ate graphs in two or three dimensions, we sometimes have to cut back the dimensionality of the space. A frequent strategy here is to use the first three eigenvectors of G-that is, the three patterns that best differentiate between situations. It is, nonetheless, additionally useful to discover different views-for instance, by choosing dimensions that maximize specific experimental contrasts of curiosity (Diedrichsen, Yokoi, & Arbuckle, 2017; Kobak et al.
Through neural stimulation to behav ior manipulation: A novel method for analyzing dynamical cognitive fashions antibiotic poisoning purchase cp-colchi overnight. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America antibiotic 5897 buy cp-colchi 0.5 mg mastercard, 103(9) bacteria reproduce using purchase cp-colchi amex, 3486�3489 antibiotic resistance and farm animals order cp-colchi 0.5mg with visa. Neural tuning to numer osity relates to perceptual tuning in 3�6year old children. Parallels in stimulus pushed oscillatory mind responses to 824 Concepts and Core Domains numerosity changes in adults and sevenmonth old infants. Symbolic estrangement: Evidence against a powerful association between numerical symbols and the quantities they symbolize. Roaring and numerical evaluation in contests between groups of feminine lions, Panthera leo. Functional and struc tural alterations of the intraparietal sulcus in a developmen tal dyscalculia of genetic origin. Supramodal numerosity selectivity of neu rons in primate prefrontal and posterior parietal cortices. Proceed ings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of Amer ica, 101(19), 7457�7462. Numerosity buildings the expres sion of quantity in lexical numbers and grammatical num ber. Grey parrot number acquisition: the inference of cardinal worth from ordinal position on the numeral record. A magnitude code common to numerosities and number sym bols in human intraparietal cortex. Deficits in action choice based on numerical information after inactiva tion of the posterior parietal cortex in monkeys. Common and distinct mind regions in each parietal and frontal cortex help symbolic and nonsymbolic quantity processing in people: A functional neuroimaging meta evaluation. Neural predictors of individual variations in response to math tutoring in major grade school youngsters. Does participation in intergroup battle rely upon numerical assessment, range location, or rank for wild chimpanzees We talk about theories and findings from cognitive science and cognitive neuroscience that shed mild on the processing stages and neural methods that permit humans to kind new conceptual combinations. We evaluate systematic and inventive applications of cognitive neurosci ence strategies, together with neuroimaging, neuropsychological patients, neurostimulation, and behavioral research, which have yielded fascinating insights into the cognitive nature and neu ral underpinnings of conceptual combination. Studies have revealed important options of the cognitive processes central to profitable conceptual combination. Despite the relative newness of those questions for cognitive neuroscience, the investiga tions we evaluate give a very strong basis for ongoing and future work that seeks to absolutely understand how the human mind can flexibly combine current ideas to form new and never before experienced mixtures at will. Investigating how individuals mix ideas can shed distinctive mild on totally different features of conceptual knowl edge, together with the cognitive mechanisms that allow the generative and versatile use of language. Why would one Conceptual Combination Our ability to assemble complicated ideas from simpler constituents, referred to as conceptual combination, is enjoyable damental to many features of cognition. One can, usually effortlessly, comprehend a novel utterance, event, or thought via the manipulation, integration, or synthesis of other easier or more familiar ideas; for instance, upon hearing a information report that because of local weather change the Pacific Northwest robin hawk is underneath threat of extinc tion, you might assemble considered one of a quantity of believable inter pretations of the which means of robin hawk (see figure seventy one. In order to understand such novel concepts, one must recruit a series of cognitive processes that may embrace identifying combinable features of the attributing and receiving ideas; choosing which of those options are to be transferred between ideas; integrating the selected features into a unitary conceptual representa tion; and confirming the plausibility of the resulting con cept. We suggest that questions that come up when considering the processes and resulting representa tions of conceptual combination could help shed light on-or a minimum of, recommend traces of fruitful inquiry into- more fundamental questions of conceptual representation. For example, what conceptual buildings are versatile sufficient to allow for the decomposition and recomposi tion of features into novel combos In addition, some of the processes that govern the integration of easy concepts (such as finger and lime) into complex ideas (such as a finger lime) may also govern how simple sensory features (such as spherical, tart, and green) are integrated into so called easy concepts (such as lime). In other phrases, combination happens at multiple levels of semantic processing, even for so referred to as easy concepts. As such, we will potentially advance our understanding of conceptual processing of all sorts by asking questions about how ideas are combined.
This proactive govt system thus supplies the flexibility to flexibly management behav ior by rapidly recreating new actors yielding to switch across learned task units according to antimicrobial nanoparticles order 0.5mg cp-colchi exterior cues infection 17 purchase cp-colchi. This type of executive management has also been termed episodic management infection outbreak order cp-colchi 0.5mg fast delivery, in the sense that it allows the training and upkeep of task sets guiding ongoing behav ior over time virus killing dogs buy 0.5mg cp-colchi visa, along with their retrieval (through actor creation) with respect to episodic occurrences of external cues (Koechlin, Ody, & Kouneiher, 2003; Koechlin & Summerfield, 2007). Under its intrinsic computational constraints (forward and factual inferences only), this computational model optimally uses external cues along with motion outcomes for adapting to environments featuring each new and recurrent situations. As described above, contextual fashions are learned in order that these cues replicate any stimuli acting as predictors of task set reliability. This scheme leaves open the likelihood that the same stimulus is involved in each contextual and selective models. B, Diagram exhibiting inferential and inhibition processes composing the monkey prefrontal function (square: task units saved in long-term memory). Inferential and inhibition processes are much like those in rodents (see figure 38. Contextual models even have a serious position in shaping actor creation: the mixture of task sets in long-term memory is now weighted by current exterior cues based on contextual models. As a result, new actors could additionally be created as instantly dependable (p(0) > 1 - p(0); see text). In that event the exploration period is skipped, yielding to the power to recreate new actors far more rapidly. However, empirical proof is that within the presence of such predictive mixtures. Yet these hierarchical structures favor the generalization of subordinate stimulus-action mappings to new combinations (Collins & Frank, 2013). These buildings are conditionally formed through hierarchical inferential processes upon the assumption that external contingencies stay steady over time (Collins & Frank, 2013)-that is, upon the inference that the state of affairs remains unchanged and, consequently, that the same task set is maintained because the actor driving ongoing behav ior. Such hierarchical selective models are thus realized and embedded within task sets and allow switching throughout motion chunks based on immediate cues inside the similar actor task set. This hierarchical form of government management thus varieties an intermediate management stage operating throughout hierarchical ranges and embedded within the episodic management of task units working alongside the temporal dimension (Koechlin, 2007; Koechlin, Ody, & Kouneiher, 2003; Koechlin & Summerfield, 2007). The Human Prefrontal Cortex: Executive Control as Counterfactual Inferences the monkey government system described above has one main limitation. Inferences in regards to the perpetuation versus termination of the current state of affairs yielding to keep the identical actor or to create a new one are solely factual: such inferences bear only upon the actor reliability, primarily based on its predictive and contextual model. These counterfactual inferences are in a position to infer online concomitantly when to change the actor and which previously discovered task units may be selected as the brand new actor. Optimally, counterfactual inferences should bear upon the whole repertoire of stored task sets. Accordingly, counterfactual 460 Neuroscience, Cognition, and Computation: Linking Hypotheses inferences are assumed to develop solely over a limited number of task units, forming the inferential buffer. One would possibly think about the inferential buffer as forming a worldwide actor guiding behav ior by mixing online monitored task units over the buffer with respect to their relative reliability (Doya et al. Collins and Koechlin (2012) showed that this hypothesis is inconsistent with human behavioral per for mance in sequential choice tasks. This is also theoretically suboptimal as a outcome of the global actor may be inferred as reliable with only unreliable task units, whereas one other task set saved in longterm reminiscence however outside the inferential buffer could be dependable. More optimally, the human govt system is assumed to concurrently infer the reliability of every monitored task set i, and when none are inferred as being reliable (more probably not applicable than applicable to the current state of affairs, i. When conversely one (i0) is inferred as being reliable (ti0 > 1- ti0 or, equivalently, ti0 > 1/ 2), the others are needed unreliable, even when thought-about collectively: by construction, certainly, inferred reliabilities sum as a lot as 1 or much less, as the present situation might match no monitored task units (Collins & Koechlin, 2012; Koechlin, 2014). Accordingly, the reliable task set turns into the actor guiding behav ior and learning external contingencies by adjusting its selective, predictive, and contextual mannequin the inferential buffer is thus assumed to comprise the actor plus numerous various task units, which we discuss with because the counterfactual task sets. The actor might thus get replaced quite than adjusted either by retrieving and switching to a dependable counterfactual task set or by creating a brand new task set from long-term memory, as described above (figure 38. In the previous case, the executive system continues to operate in the exploitation mode as a outcome of the model new actor is initially deemed dependable. In the latter case, the new actor could additionally be created as unreliable, by which occasion the inferential system switches into the exploration mode.
Purchase 0.5mg cp-colchi fast delivery. Listerine Original Mouthwash review by Genuine Review genuinereview.