CLINICAL,FORENSIC,AND ETHICS CONSULTATION IN MENTAL HEALTH
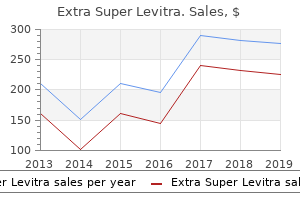
Extra Super Levitra
"Purchase 100mg extra super levitra free shipping, erectile dysfunction caused by ssri".
By: L. Hauke, M.A., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Virginia Tech Carilion School of Medicine and Research Institute
In the determination of the appropriateness of early versus delayed surgery erectile dysfunction latest medicine extra super levitra 100mg amex,43-45 the next principles should be observed: � Avoid extended operations in the early phases of mind injury impotence ring buy extra super levitra in india, when the brain is very prone to hypoxia and reduces in cerebral perfusion stress erectile dysfunction treatment without medication quality extra super levitra 100mg. Acute mind harm is finest managed with early treatment of mind compression and closure of compound wounds erectile dysfunction interesting facts discount 100 mg extra super levitra otc, adopted by cautious monitoring in the intensive care unit to control intracranial strain and cerebral perfusion. OpticNerveInjury Management of traumatic optic nerve damage remains controversial, and the talk whether or not statement alone is healthier than steroids, surgical decompression, or a combination of the 2 remains unresolved. Urgent operative intervention could also be essential for injuries to different body systems, such as the thorax and stomach. Interdisciplinary session determines the order of priorities and whether or not simultaneous or sequential operations should be carried out. Soft tissue lacerations of the pores and skin and oral mucosa should be closed as soon as possible to scale back the dangers of an infection and further tissue loss. Exposed dura and mind, naked cortical bone, and major vessels need to be coated urgently. At the identical time, repair of important structures such as the eyelids, nerves, and salivary ducts may be undertaken. Delayed definitive surgical procedure may also be timed to coincide with different, less pressing operative procedures. The cranio-orbital interface, which is the junction between the anterior cranial fossa and frontal sinus above and the orbits and nasoethmoid region beneath. Posteriorly, fractures of the orbital apex and orbital roof may compromise the oculomotor nerves, the optic nerve, and ocular place and motility. The zygoma, which articulates with the sphenoid, maxilla, and frontal and temporal bones. A right and steady arch place determines the lateral midface projection and midface width. The mandibular condyles, which demarcate the posterolateral limit of the center fossa and the exterior auditory canal. Timing of Repair There may be opportunities for early repair at the time of emergency procedures without unduly extending operative time. For example, a depressed frontal bone may be elevated, dura repaired, and maybe a ruptured eye enucleated and, on the same operation, orbital fractures fixed and an examination with anesthesia undertaken to determine the extent of any associated jaw fractures. Dental impressions can be taken in preparation for definitive correction of the jaws at a later date. Some writers advocate very early definitive surgical procedure, within 24 to 48 hours as a common rule, reasoning that reconstruction should be undertaken before contractile scar tissue prevents appropriate positioning of soppy tissues, notably these within the orbit. This delay allows time for clinical stabilization of the affected person and preparation of a Craniofacial Exposures Surgical remedy is often primarily based on wide publicity of the craniofacial skeleton through a bicoronal scalp flap or periorbital, intraoral, and extraoral incisions (Video 355-1). A, A zigzag or wavy coronal incision provides a better beauty result than a straight incision. The floor marking of the frontal department of the facial nerve because it crosses the zygomatic arch is outlined by the dotted line drawn between the zygomatic tubercle and the midpoint of the ear lobe. The pericranium is incised 1 cm superficial to the superior orbital margin, and the dissection is sustained subperiosteally into the orbit; it then proceeds within the airplane deep to the superficial temporal fascia right down to the zygomatic body and arch. Keeping the incision deep to the fat pad over the superficial temporal fascia protects the frontalis branch of the facial nerve. C, the bicoronal scalp flap can be taken low enough to expose the superior orbits, nasoethmoid region, zygoma, and condyles of the mandible. From this stage the dissection proceeds subpericranially over the orbital rim and into the orbit. The supraorbital neurovascular bundle is rigorously preserved, if essential, by fracturing of the margins of the supraorbital notch with a fine osteotome. It is important to dissect strictly in opposition to the temporal fascia or to incise via the superficial layer of the temporal fascia and dissect at the subfascial fats airplane down to the zygomatic arch to protect the frontal department of the facial nerve, which lies superficially within or above the superficial temporal fascia. At the level of the zygomatic arch the periosteum is stripped with nice care, significantly from the middle and posterior thirds. This step may be difficult when the arch is fractured, and the frontalis department of the facial nerve could be broken. When orbital fractures are current, soft tissue could additionally be trapped between bony fragments, which should be separated to release the delicate tissue. The temporomandibular joint and the neck of the condyle could be approached by extension of the bicoronal flap to the lobule of the ear. Careful dissection of the soft tissue from the lateral ligaments of the temporomandibular joint capsule enables visualization of the neck of the condyle and the sigmoid notch.
A 46-year-old man sustained an L2 burst fracture 31 years beforehand and was handled by decompressive laminectomy of L2 and L3 erectile dysfunction and pregnancy buy discount extra super levitra 100mg line. He got here to our establishment with a 2-year historical past of intractable decrease back ache and an externally visible thoracic spinal deformity erectile dysfunction girlfriend order 100mg extra super levitra otc. A impotence antonym buy cheap extra super levitra on line, Lateral 36-inch standing radiograph demonstrating an L2 fracture and a 49-degree kyphotic deformity measured from the top of T12 to the underside of L4 erectile dysfunction therapy treatment 100mg extra super levitra with amex. B, Postoperative lateral 36-inch standing radiograph after pedicle subtraction osteotomy at L2, internal reduction, T12-L4 posterior fusion, and screw-rod stabilization. In patients with evidence of neural compression, sharp dissection is undertaken to cleanly dissect scar tissue from the bony margins of the previous laminectomy. The margins of the earlier laminectomy are extended with a Kerrison rongeur to permit publicity of normal dura. The earlier bone decompression is extended by bilaterally removing the remaining laminae, pars interarticularis, and inferior facets at the levels to be operated. After bone decompression, careful identification and dissection of the neural parts away from the scar tissue is then carried out. Significant epidural scar tissue can be resected with sharp instruments corresponding to a curet or scalpel or a pointy Kerrison rongeur, as described beforehand. After decompression, the thecal sac and the exiting and traversing nerve roots are widely uncovered. Care is taken to protect the ventral and lateral margins of the anulus to permit the graft material, each structural and morselized, to be contained throughout the interbody space. Once that is completed, an interbody graft is placed bilaterally as a outcome of we consider that a single cage with unilateral fusion is associated with an elevated pseudarthrosis price. The carbon fiber cages that we use have a lordotic sagittal contour with the ventral floor being 2 mm larger than the dorsal surface. In sufferers with important loss of lumbar lordosis or a constructive sagittal steadiness, correction of the deformity can be achieved with the use of lordotically formed interbody grafts. For larger grades of spondylolisthesis, the interbody graft is placed after a minimal of partial discount of the deformity has been completed. By resecting the medial features of the subjacent superior sides, manipulation of the thecal sac and nerve roots is saved to a minimum during placement of the interbody graft. After bilateral placement of the lateral fusion bone, the screws are related to one another with both plates or rods. The plates or rods are contoured within the sagittal plane to achieve lumbar lordosis. In this maneuver, distraction units are used to deliver the pedicle screws to the overcontoured rods or plates, with the amount of lordosis being increased to match that of the contoured rods or plates. If necessary, compression of the screws posteriorly may be performed to improve the extent of lordosis that can be achieved. However, such compression should be used only along side ventral interbody assist. In circumstances of spondylolisthesis, significant discount of the deformity is commonly achieved after connecting the pedicle screws to the contoured rods or plates. Two large-bore suction drains could be positioned, on the discretion of the working surgeon, and normal wound closure is then carried out in layers. The overall objective of lumbar pseudarthrosis revision surgical procedure is to optimize each mechanical fixation and the environment for bone therapeutic. Strict adherence to the basic techniques that promote bone healing, similar to proper graft placement and recipient bed preparation, is important for obtaining profitable fusion. In the lumbar spine, biomechanical optimization may be achieved by restoring the sagittal stability of the spine and by load sharing through the addition of internal fixation units. The presence of a considerably positive sagittal balance places a substantially increased flexion moment on posterior instrumentation. Preoperative axial proton density magnetic resonance picture (A), anteroposterior radiograph (B), and lateral radiograph (C) of a 31-year-old woman who had undergone an tried posterior lumbar interbody fusion 1 yr beforehand. She had complaints of intractable decrease again pain, proper lower extremity weak spot, right lower extremity numbness, and problem urinating. Imaging demonstrated migration of the cage into the spinal canal with compression of neural elements. A unilateral screw-rod construct is demonstrated with a laterally misplaced S1 pedicle screw. Bilateral posterolateral fusion with autologous iliac crest graft and bilateral pedicle screw-rod stabilization were carried out.
Buy on line extra super levitra. Diabetes Causes Sexual Dysfunction & treatment. ( DOCTOR'S TIPS ).
The biomechanical power of the transiliac bar is comparable with that of different primary iliac fixation methods importance of being earnest effective extra super levitra 100mg, and charges of successful arthrodesis have been reported in one collection to be greater than 95% erectile dysfunction fertility treatment generic 100 mg extra super levitra otc. Various construct combos consisting of bilateral sacral and iliac screws have repeatedly yielded excellent clinical outcomes and demonstrated that iliac screws are an efficient technique of protecting S1 screws (no case of breakage erectile dysfunction definition purchase extra super levitra 100mg visa, loosening erectile dysfunction best medication discount extra super levitra 100 mg online, or pullout) and attaining arthrodesis throughout the lumbosacral junction. Arthrodesis charges have been reported as high as 95% on long-term follow-up in some series, and in other sequence, pseudoarthrosis rates of 5% to 24% have been reported. In order to ensure perfect spinopelvic alignment and obtain optimal surgical deformity correction, the patient is positioned inclined, and bolsters are applied to maximize lumbar lordosis. Iliac Screws Modification of the Galveston approach resulted in a technically superior process: iliac screw fixation. The availability of various connectors and polyaxial screw heads provided for modularity and minimized the need for intensive rod contouring. It is essential to take away enough bone at the start line that the screw head sits flush with probably the most outstanding level of the ilium. Failure to Iliosacral Screws In comparability with S1 pedicle screws, iliosacral screws supply increased caudal buy and energy by passing lateral to medial via each cortices of the iliac crest, through the S1 pedicle, and into the physique of the sacrum. Clinical and biomechanical analyses have demonstrated iliosacral screws to be comparable to Galveston rods with regard to most stiffness at failure however with superior pullout strength, which finally ends up in low rates of pseudoarthrosis. A gear-shift probe is inserted into the place to begin and aimed 30 to forty five levels medial to lateral and 30 to 45 degrees rostral to caudal. Under the guidance of anteroposterior fluoroscopy, the probe is inserted to a depth of 60 to 70 mm towards a target simply above the sciatic notch towards the anterior-inferior iliac spine. As the probe is passed, care must be taken to avoid violation of the acetabulum or the sciatic notch. Penetration of the sciatic notch may lead to damage to the sciatic nerve or the superior gluteal vessels. Pelvic inlet and obturator views may also be helpful in guiding the screw trajectory. Alternatively, image steerage with intraoperative computed tomographic scanning, commonly used at our establishment, is an effective methodology for reaching perfect screw placement. A ball-tipped probe is then inserted and used to palpate for cortical breech, and an undersized tap is launched. The screw is then inserted and affixed to the proximal construct both instantly or via a lateral connector (Video 332-1). Again, image steering with intraoperative computed tomographic scanning is an efficient methodology for ensuring perfect screw placement. After the opening is palpated and tapped, the screw is inserted and may align nicely with the rostral S1 screws. No neurovascular or visceral constructions were violated, as judged from postoperative scans. As supplementing constructs after the discount of high-grade spondylolisthesis, three-column osteotomies in the lower lumbar backbone to correct deformity also qualify for pelvic fixation. The final determinant of long-term implant survival is the achievement of biologic arthrodesis. Traditional iliac screw placement requires vital delicate tissue dissection; the potential want for added offset connectors, the prominence of screws, the incidence of sacroiliac joint inflammation, and a high incidence of painful loosening typically necessitate hardware removing or revision. A pilot hole is created with a high-speed drill to penetrate the outer cortex, and a gear-shift probe is inserted, aiming toward the greater trochanter. The trajectory is roughly forty five levels medial to lateral and 30 levels rostral to caudal. The probe is then handed by way of the sacroiliac joint into the ilium to roughly 70 or 80 mm. If needed, a mallet or a low-speed drill can be utilized to faucet through the sacroiliac joint. Pelvic fixation in spine surgery-historical overview, indications, biomechanical relevance, and present methods. Comparison of pelvic fixation techniques in neuromuscular spinal deformity correction: Galveston rod versus iliac and lumbosacral screws.
Mechanisms of major blast-induced traumatic mind harm: insights from shock-wave research vyvanse erectile dysfunction treatment proven extra super levitra 100mg. Neuropathology and stress within the pig brain resulting from low-impulse noise publicity erectile dysfunction numbness discount extra super levitra 100 mg line. Mechanisms and pathophysiology of the low-level blast mind damage in animal models injections for erectile dysfunction that truly work discount extra super levitra 100 mg visa. Distinct patterns of expression of traumatic mind injury biomarkers after blast publicity: position of compromised cell membrane integrity impotence of proofreading poem cheap 100mg extra super levitra. A mannequin of low-level major blast mind trauma results in cytoskeletal proteolysis and persistent practical impairment within the absence of lung barotrauma. Time-dependent changes in serum biomarker ranges after blast traumatic brain damage. Viscoelastic properties of human cerebellum utilizing magnetic resonance elastography. Cerebrocerebellar hypometabolism associated with repetitive blast exposure mild traumatic brain injury in 12 Iraq war Veterans with persistent post-concussive symptoms. Involvement of the central nervous system within the general response to pulmonary blast harm. Left ventricular receptors: physiological controllers or pathological curiosities Physiological adjustments in pigs exposed to a blast wave from a detonating high-explosive cost. Reflex nature of the cardiorespiratory response to major thoracic blast injury within the anaesthetised rat. Overpressure blast-wave induced brain damage elevates oxidative stress in the hypothalamus and catecholamine biosynthesis within the rat adrenal medulla. Blast Injuries and Blast-Induced Neurotrauma: Overview of Pathophysiology and Experimental Knowledge-Models and Findings. An introductory characterization of a combat-casualty-care related swine mannequin of closed head damage resulting from publicity to explosive blast. Fluid shear stress will increase neutrophil activation through platelet-activating issue. Endothelial activation and chemoattractant expression are early processes in isolated blast brain harm. Exposure of the thorax to a sublethal blast wave causes a hydrodynamic pulse that results in perivenular inflammation within the brain. Relationship between orientation to a blast and stress wave propagation inside the rat mind. Measurement of blast wave by a miniature fiber optic strain transducer in the rat mind. Low ranges of blast elevate intracranial stress and impair cognitive function in rats. Effect of blast exposure on the mind construction and cognition in Macaca fascicularis. Acute mitochondrial dysfunction after blast publicity: potential role of mitochondrial glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase. Cognitive deficits following blast injury-induced neurotrauma: attainable involvement of nitric oxide. Blast publicity causes early and persistent aberrant phospho- and cleaved-tau expression in a murine mannequin of delicate blast-induced traumatic mind harm. Long-term consequences of single and a number of delicate blast publicity on select physiological parameters and blood-based biomarkers. Brain damage: neuroinflammation, cognitive deficit, and magnetic resonance imaging in a model of blast induced traumatic mind damage. Neuro-glial and systemic mechanisms of pathological responses in rat models of main blast overpressure in comparability with "composite" blast. Blast induces oxidative stress, irritation, neuronal loss and subsequent short-term memory impairment in rats. Stress and traumatic mind damage; a behavioral, proteomics and histological examine.